NestJS Day 5: What are Pipes?

Abstract
This is a concise, summarized approach to learn NestJS. For more in-depth knowledge about NestJS, visit the official NestJS documentation.
Pipes in NestJS are powerful components that operate on the arguments being processed by controller route handlers. They have two primary use cases: transformation (converting input data to the desired form) and validation (evaluating input data and passing it through unchanged if valid, or throwing an exception if invalid).
Table of Contents
- What are Pipes?
- Built-in Pipes
- Binding Pipes
- Transformation Use Cases
- Validation Use Cases
- Custom Pipes
- Schema-based Validation
- Class Validator Integration
- Global Pipes
- Advanced Pipe Techniques
- Best Practices
- Real-world Examples
1. What are Pipes?
Pipes are classes annotated with the @Injectable() decorator that implement the PipeTransform interface. They run inside the exceptions zone, meaning when a pipe throws an exception, it’s handled by the exceptions layer and no controller method is executed afterward.
As you can see there are a bunch of decorators and their interface to remember, I created this small diagram to help you remember them:
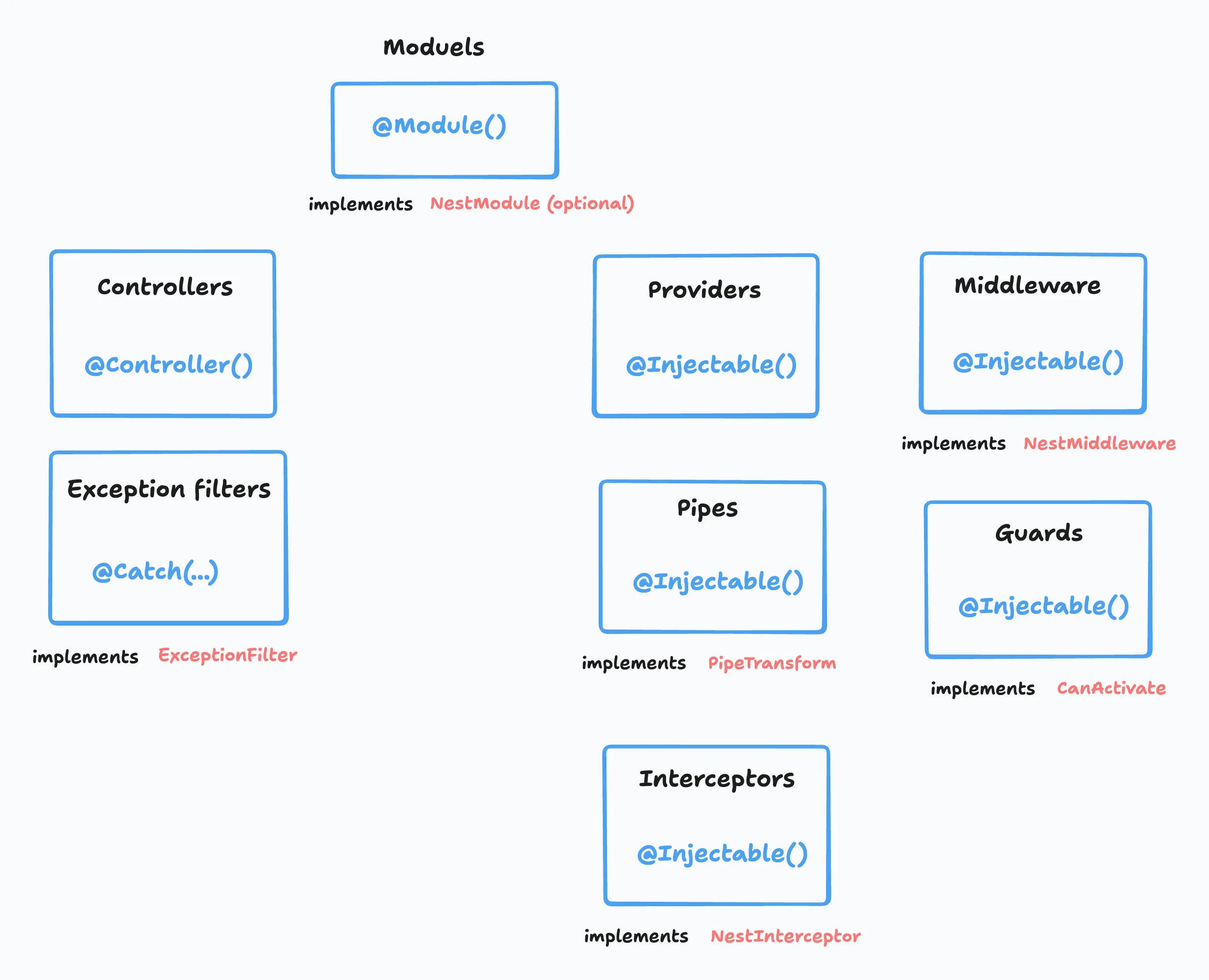
Key Characteristics:
- Transform data: Convert input data to desired format (string to integer)
- Validate data: Ensure input data meets certain criteria
- Run before method execution: Pipes intercept arguments before they reach route handlers
- Exception handling: Failed validation/transformation throws exceptions automatically
- Reusable: Can be applied at different scopes (parameter, method, controller, global)
Pipe Interface
Every pipe must implement the PipeTransform interface:
import { PipeTransform, ArgumentMetadata } from "@nestjs/common";
export interface PipeTransform<T = any, R = any> { transform(value: T, metadata: ArgumentMetadata): R;}The transform() method has two parameters:
value: The currently processed method argumentmetadata: The metadata of the currently processed method argument
2. Built-in Pipes
NestJS provides several built-in pipes available out-of-the-box:
Core Built-in Pipes
import { ValidationPipe, ParseIntPipe, ParseFloatPipe, ParseBoolPipe, ParseArrayPipe, ParseUUIDPipe, ParseEnumPipe, DefaultValuePipe, ParseFilePipe, ParseDatePipe,} from "@nestjs/common";ParseIntPipe
Converts string parameters to integers and validates they are numeric:
// Basic usage@Get(':id')async findOne(@Param('id', ParseIntPipe) id: number) { return this.catsService.findOne(id);}
// With custom error status@Get(':id')async findOne( @Param('id', new ParseIntPipe({ errorHttpStatusCode: HttpStatus.NOT_ACCEPTABLE })) id: number,) { return this.catsService.findOne(id);}
// Query parameter example@Get()async findAll(@Query('age', ParseIntPipe) age: number) { return this.catsService.findByAge(age);}ParseBoolPipe
Converts string values to boolean:
@Get()async findAll( @Query('activeOnly', ParseBoolPipe) activeOnly: boolean) { return this.catsService.findAll(activeOnly);}
// Accepts: 'true', 'false', '1', '0'// GET /cats?activeOnly=true// GET /cats?activeOnly=1ParseUUIDPipe
Validates and parses UUID strings:
@Get(':uuid')async findOne(@Param('uuid', ParseUUIDPipe) uuid: string) { return this.catsService.findOne(uuid);}
// Specific UUID version@Get(':uuid')async findOne( @Param('uuid', new ParseUUIDPipe({ version: '4' })) uuid: string) { return this.catsService.findOne(uuid);}ParseEnumPipe
Validates that a value is part of an enum:
enum Status { ACTIVE = 'active', INACTIVE = 'inactive', PENDING = 'pending'}
@Get()async findByStatus( @Query('status', new ParseEnumPipe(Status)) status: Status) { return this.catsService.findByStatus(status);}DefaultValuePipe
Provides default values for missing parameters:
@Get()async findAll( @Query('activeOnly', new DefaultValuePipe(false), ParseBoolPipe) activeOnly: boolean, @Query('page', new DefaultValuePipe(0), ParseIntPipe) page: number,) { return this.catsService.findAllPagination({ activeOnly, page });}ParseArrayPipe
Converts comma-separated values to arrays:
@Get()async findByTags( @Query('tags', new ParseArrayPipe({ items: String, separator: ',' })) tags: string[]) { return this.catsService.findByTags(tags);}
// GET /cats?tags=persian,siamese,maine-coon// Result: ['persian', 'siamese', 'maine-coon']NestJS Built-in Pipes Cheat Sheet
1. ValidationPipe
Purpose: Validates request data against class-validator decorators and transforms plain objects to class instances.
Use Cases:
- Form validation
- API request body validation
- Query parameter validation
- Auto-transformation of incoming data
Basic Usage:
// Global usageapp.useGlobalPipes(new ValidationPipe());
// Route-level usage@Post()@UsePipes(new ValidationPipe())createUser(@Body() createUserDto: CreateUserDto) { return this.userService.create(createUserDto);}
// Parameter-level usage@Post()createUser(@Body(new ValidationPipe()) createUserDto: CreateUserDto) { return this.userService.create(createUserDto);}Common Options:
new ValidationPipe({ whitelist: true, // Strip non-whitelisted properties forbidNonWhitelisted: true, // Throw error for non-whitelisted properties transform: true, // Auto-transform payloads to DTO instances disableErrorMessages: false, // Disable detailed error messages validateCustomDecorators: true, // Enable custom validators});2. ParseIntPipe
Purpose: Transforms string parameters to integers and validates they are valid numbers.
Use Cases:
- URL path parameters (e.g.,
/users/:id) - Query parameters that should be numbers
- Route parameters requiring integer validation
Usage:
// Path parameter@Get(':id')findOne(@Param('id', ParseIntPipe) id: number) { return this.userService.findOne(id);}
// Query parameter@Get()findAll(@Query('page', ParseIntPipe) page: number) { return this.userService.findAll(page);}
// With custom error message@Get(':id')findOne(@Param('id', new ParseIntPipe({ errorHttpStatusCode: HttpStatus.NOT_ACCEPTABLE })) id: number) { return this.userService.findOne(id);}3. ParseFloatPipe
Purpose: Transforms string parameters to floating-point numbers.
Use Cases:
- Price calculations
- Coordinates (latitude, longitude)
- Percentage values
- Any decimal number inputs
Usage:
// Query parameter for price filtering@Get('products')getProducts(@Query('minPrice', ParseFloatPipe) minPrice: number) { return this.productService.findByMinPrice(minPrice);}
// Path parameter for coordinates@Get('location/:lat/:lng')getLocation( @Param('lat', ParseFloatPipe) latitude: number, @Param('lng', ParseFloatPipe) longitude: number) { return this.locationService.findByCoordinates(latitude, longitude);}4. ParseBoolPipe
Purpose: Transforms string values to boolean values.
Use Cases:
- Feature toggles
- Filter flags (active/inactive)
- Boolean query parameters
- Configuration options
Usage:
// Query parameter for filtering@Get('users')getUsers(@Query('isActive', ParseBoolPipe) isActive: boolean) { return this.userService.findByStatus(isActive);}
// Feature toggle@Get('products')getProducts(@Query('includeDiscounted', ParseBoolPipe) includeDiscounted: boolean) { return this.productService.findAll(includeDiscounted);}Accepted Values: true, false, 'true', 'false', '1', '0', 1, 0
5. ParseArrayPipe
Purpose: Transforms comma-separated strings or arrays into typed arrays.
Use Cases:
- Multiple IDs selection
- Tag filtering
- Multiple category selection
- Bulk operations
Usage:
// Query parameter for multiple IDs@Get()findByIds(@Query('ids', new ParseArrayPipe({ items: Number })) ids: number[]) { return this.userService.findByIds(ids);}
// String array@Get('products')findProducts(@Query('tags', new ParseArrayPipe({ items: String, separator: ',' })) tags: string[]) { return this.productService.findByTags(tags);}
// With custom separator@Get()findUsers(@Query('roles', new ParseArrayPipe({ items: String, separator: '|' })) roles: string[]) { return this.userService.findByRoles(roles);}6. ParseUUIDPipe
Purpose: Validates and ensures parameters are valid UUIDs.
Use Cases:
- Database primary keys using UUIDs
- Session IDs
- API keys validation
- Resource identifiers
Usage:
// Path parameter validation@Get(':id')findOne(@Param('id', ParseUUIDPipe) id: string) { return this.userService.findOne(id);}
// Specific UUID version@Get(':id')findOne(@Param('id', new ParseUUIDPipe({ version: '4' })) id: string) { return this.userService.findOne(id);}
// Query parameter@Get()findBySession(@Query('sessionId', ParseUUIDPipe) sessionId: string) { return this.sessionService.findBySessionId(sessionId);}Supported Versions: '3', '4', '5', 'all' (default)
7. ParseEnumPipe
Purpose: Validates that a parameter value exists in a specified enum.
Use Cases:
- Status filtering (ACTIVE, INACTIVE, PENDING)
- User roles validation
- Order status
- Category types
Usage:
// Define enumenum UserRole { ADMIN = 'admin', USER = 'user', MODERATOR = 'moderator'}
enum Status { ACTIVE = 'active', INACTIVE = 'inactive', PENDING = 'pending'}
// Usage in controller@Get()findByRole(@Query('role', new ParseEnumPipe(UserRole)) role: UserRole) { return this.userService.findByRole(role);}
@Get('orders')getOrders(@Query('status', new ParseEnumPipe(Status)) status: Status) { return this.orderService.findByStatus(status);}8. DefaultValuePipe
Purpose: Provides default values for parameters when they are undefined or null.
Use Cases:
- Pagination defaults
- Default sorting options
- Optional query parameters
- Configuration defaults
Usage:
// Pagination defaults@Get()findAll( @Query('page', new DefaultValuePipe(1), ParseIntPipe) page: number, @Query('limit', new DefaultValuePipe(10), ParseIntPipe) limit: number) { return this.userService.findAll(page, limit);}
// Default sorting@Get('products')getProducts( @Query('sortBy', new DefaultValuePipe('createdAt')) sortBy: string, @Query('order', new DefaultValuePipe('DESC')) order: string) { return this.productService.findAll(sortBy, order);}
// Boolean default@Get()getUsers(@Query('includeInactive', new DefaultValuePipe(false), ParseBoolPipe) includeInactive: boolean) { return this.userService.findAll(includeInactive);}9. ParseFilePipe
Purpose: Validates uploaded files including size, type, and other constraints.
Use Cases:
- File upload validation
- Image upload restrictions
- Document type validation
- File size limitations
Usage:
// Basic file validation@Post('upload')@UseInterceptors(FileInterceptor('file'))uploadFile(@UploadedFile(ParseFilePipe) file: Express.Multer.File) { return this.fileService.upload(file);}
// With validators@Post('upload-image')@UseInterceptors(FileInterceptor('image'))uploadImage( @UploadedFile( new ParseFilePipe({ validators: [ new MaxFileSizeValidator({ maxSize: 1024 * 1024 * 5 }), // 5MB new FileTypeValidator({ fileType: /^image\/(jpeg|png|gif)$/ }) ] }) ) file: Express.Multer.File) { return this.imageService.upload(file);}
// Optional file upload@Post('upload-optional')@UseInterceptors(FileInterceptor('file'))uploadOptional( @UploadedFile( new ParseFilePipe({ fileIsRequired: false, validators: [ new MaxFileSizeValidator({ maxSize: 1024 * 1024 * 2 }) ] }) ) file?: Express.Multer.File) { return file ? this.fileService.upload(file) : { message: 'No file uploaded' };}Built-in Validators:
MaxFileSizeValidator: File size limitsFileTypeValidator: MIME type validation
10. ParseDatePipe
Purpose: Transforms string parameters into Date objects with validation.
Use Cases:
- Date range filtering
- Scheduling parameters
- Event date validation
- Timestamp parsing
Usage:
// Query parameter for date filtering@Get('events')getEvents( @Query('startDate', ParseDatePipe) startDate: Date, @Query('endDate', ParseDatePipe) endDate: Date) { return this.eventService.findByDateRange(startDate, endDate);}
// Path parameter@Get('schedule/:date')getSchedule(@Param('date', ParseDatePipe) date: Date) { return this.scheduleService.findByDate(date);}
// Optional date with default@Get('reports')getReports( @Query('from', new DefaultValuePipe(new Date()), ParseDatePipe) from: Date) { return this.reportService.findFrom(from);}Accepted Formats:
- ISO 8601 strings:
2023-12-25T10:30:00Z - Date strings:
2023-12-25 - Timestamp numbers:
1703505000000
3. Binding Pipes
Pipes can be bound at different scopes to control where they apply:
Parameter-scoped Pipes
Applied to individual parameters:
// Class binding (recommended)@Get(':id')async findOne(@Param('id', ParseIntPipe) id: number) { return this.catsService.findOne(id);}
// Instance binding (for custom configuration)@Get(':id')async findOne( @Param('id', new ParseIntPipe({ errorHttpStatusCode: HttpStatus.NOT_ACCEPTABLE })) id: number,) { return this.catsService.findOne(id);}Method-scoped Pipes
Applied to all parameters of a method:
@Post()@UsePipes(ValidationPipe)async create(@Body() createCatDto: CreateCatDto) { return this.catsService.create(createCatDto);}
// Multiple pipes@Post()@UsePipes(ValidationPipe, TransformPipe)async create(@Body() createCatDto: CreateCatDto) { return this.catsService.create(createCatDto);}Controller-scoped Pipes
Applied to all methods in a controller:
@Controller("cats")@UsePipes(ValidationPipe)export class CatsController { @Post() async create(@Body() createCatDto: CreateCatDto) { return this.catsService.create(createCatDto); }
@Put(":id") async update(@Param("id") id: string, @Body() updateCatDto: UpdateCatDto) { return this.catsService.update(id, updateCatDto); }}Global Pipes
Applied to every route handler across the entire application:
// main.ts - Instance bindingasync function bootstrap() { const app = await NestFactory.create(AppModule); app.useGlobalPipes(new ValidationPipe()); await app.listen(3000);}
// app.module.ts - Dependency injection (recommended)@Module({ providers: [ { provide: APP_PIPE, useClass: ValidationPipe, }, ],})export class AppModule {}4. Transformation Use Cases
Transformation pipes convert input data to the desired format:
Basic String to Number Transformation
// Custom ParseIntPipe implementationimport { PipeTransform, Injectable, ArgumentMetadata, BadRequestException } from '@nestjs/common';
@Injectable()export class ParseIntPipe implements PipeTransform<string, number> { transform(value: string, metadata: ArgumentMetadata): number { const val = parseInt(value, 10); if (isNaN(val)) { throw new BadRequestException('Validation failed (numeric string is expected)'); } return val; }}
// Usage@Get(':id')async findOne(@Param('id', ParseIntPipe) id: number) { console.log(typeof id); // number return this.catsService.findOne(id);}User Entity Transformation
Transform an ID to a full user entity:
@Injectable()export class UserByIdPipe implements PipeTransform<string, Promise<UserEntity>> { constructor(private usersService: UsersService) {}
async transform(value: string, metadata: ArgumentMetadata): Promise<UserEntity> { const user = await this.usersService.findById(value); if (!user) { throw new NotFoundException(`User with ID ${value} not found`); } return user; }}
// Usage - parameter becomes the full user entity@Get(':id')async getUser(@Param('id', UserByIdPipe) user: UserEntity) { return user; // Full user object, not just the ID}Trim and Normalize String
@Injectable()export class TrimPipe implements PipeTransform<string, string> { transform(value: string, metadata: ArgumentMetadata): string { return typeof value === 'string' ? value.trim().toLowerCase() : value; }}
@Get()async search(@Query('q', TrimPipe) query: string) { return this.searchService.search(query);}5. Validation Use Cases
Validation pipes ensure data meets specific criteria before processing:
Simple Validation Pipe
@Injectable()export class ValidationPipe implements PipeTransform { transform(value: any, metadata: ArgumentMetadata) { // Simple validation logic if (!value) { throw new BadRequestException("Value is required"); } return value; }}Age Validation Pipe
@Injectable()export class AgeValidationPipe implements PipeTransform<number, number> { transform(value: number, metadata: ArgumentMetadata): number { if (value < 0 || value > 150) { throw new BadRequestException('Age must be between 0 and 150'); } return value; }}
@Post()async create( @Body('age', ParseIntPipe, AgeValidationPipe) age: number, @Body() createCatDto: CreateCatDto) { return this.catsService.create({ ...createCatDto, age });}6. Custom Pipes
Creating custom pipes for specific business logic:
File Size Validation Pipe
@Injectable()export class FileSizeValidationPipe implements PipeTransform { constructor(private readonly maxSizeInBytes: number) {}
transform(value: Express.Multer.File, metadata: ArgumentMetadata) { if (value.size > this.maxSizeInBytes) { throw new BadRequestException( `File size exceeds limit of ${this.maxSizeInBytes} bytes` ); } return value; }}
// Usage@Post('upload')@UseInterceptors(FileInterceptor('file'))async uploadFile( @UploadedFile(new FileSizeValidationPipe(1024 * 1024)) // 1MB limit file: Express.Multer.File) { return this.fileService.save(file);}Password Strength Validation Pipe
@Injectable()export class PasswordValidationPipe implements PipeTransform<string, string> { transform(value: string, metadata: ArgumentMetadata): string { const passwordRegex = /^(?=.*[a-z])(?=.*[A-Z])(?=.*\d)(?=.*[@$!%*?&])[A-Za-z\d@$!%*?&]{8,}$/;
if (!passwordRegex.test(value)) { throw new BadRequestException( 'Password must contain at least 8 characters, including uppercase, lowercase, number, and special character' ); }
return value; }}
@Post('register')async register( @Body('password', PasswordValidationPipe) password: string, @Body() userData: CreateUserDto) { return this.authService.register({ ...userData, password });}7. Schema-based Validation
Using external libraries for comprehensive validation:
Zod Schema Validation
Install Zod first:
npm install --save zodCreate a Zod validation pipe:
import { PipeTransform, ArgumentMetadata, BadRequestException,} from "@nestjs/common";import { ZodSchema } from "zod";
export class ZodValidationPipe implements PipeTransform { constructor(private schema: ZodSchema) {}
transform(value: unknown, metadata: ArgumentMetadata) { try { const parsedValue = this.schema.parse(value); return parsedValue; } catch (error) { throw new BadRequestException("Validation failed"); } }}Define Zod schema:
import { z } from "zod";
export const createCatSchema = z .object({ name: z.string().min(1).max(50), age: z.number().int().min(0).max(30), breed: z.string().min(1), isActive: z.boolean().default(true), }) .required();
export type CreateCatDto = z.infer<typeof createCatSchema>;Use with controller:
@Post()@UsePipes(new ZodValidationPipe(createCatSchema))async create(@Body() createCatDto: CreateCatDto) { return this.catsService.create(createCatDto);}Joi Schema Validation
import * as Joi from "joi";
export const createCatSchema = Joi.object({ name: Joi.string().required().min(1).max(50), age: Joi.number().integer().min(0).max(30).required(), breed: Joi.string().required(), isActive: Joi.boolean().default(true),});
@Injectable()export class JoiValidationPipe implements PipeTransform { constructor(private schema: Joi.ObjectSchema) {}
transform(value: any, metadata: ArgumentMetadata) { const { error, value: validatedValue } = this.schema.validate(value); if (error) { throw new BadRequestException("Validation failed"); } return validatedValue; }}8. Class Validator Integration
Using class-validator and class-transformer for decorator-based validation:
Installation
npm install --save class-validator class-transformerDTO with Validation Decorators
import { IsString, IsInt, IsBoolean, IsOptional, Min, Max, Length, IsEmail, IsEnum, ValidateNested, Type,} from "class-validator";
export enum CatBreed { PERSIAN = "persian", SIAMESE = "siamese", MAINE_COON = "maine_coon",}
export class OwnerDto { @IsString() @Length(2, 50) name: string;
@IsEmail() email: string;}
export class CreateCatDto { @IsString() @Length(1, 50) name: string;
@IsInt() @Min(0) @Max(30) age: number;
@IsEnum(CatBreed) breed: CatBreed;
@IsBoolean() @IsOptional() isActive?: boolean = true;
@ValidateNested() @Type(() => OwnerDto) owner: OwnerDto;}Custom Validation Pipe with Class Validator
import { PipeTransform, Injectable, ArgumentMetadata, BadRequestException,} from "@nestjs/common";import { validate } from "class-validator";import { plainToInstance } from "class-transformer";
@Injectable()export class ValidationPipe implements PipeTransform<any> { async transform(value: any, { metatype }: ArgumentMetadata) { if (!metatype || !this.toValidate(metatype)) { return value; }
const object = plainToInstance(metatype, value); const errors = await validate(object);
if (errors.length > 0) { const errorMessage = errors .map((error) => Object.values(error.constraints || {})) .flat() .join(", ");
throw new BadRequestException(`Validation failed: ${errorMessage}`); }
return object; }
private toValidate(metatype: Function): boolean { const types: Function[] = [String, Boolean, Number, Array, Object]; return !types.includes(metatype); }}Usage with Detailed Error Handling
@Injectable()export class DetailedValidationPipe implements PipeTransform<any> { async transform(value: any, { metatype }: ArgumentMetadata) { if (!metatype || !this.toValidate(metatype)) { return value; }
const object = plainToInstance(metatype, value); const errors = await validate(object);
if (errors.length > 0) { const formattedErrors = errors.map((error) => ({ field: error.property, errors: Object.values(error.constraints || {}), value: error.value, }));
throw new BadRequestException({ message: "Validation failed", errors: formattedErrors, }); }
return object; }
private toValidate(metatype: Function): boolean { const types: Function[] = [String, Boolean, Number, Array, Object]; return !types.includes(metatype); }}Parameter-scoped Class Validation
@Post()async create( @Body(new ValidationPipe()) createCatDto: CreateCatDto) { return this.catsService.create(createCatDto);}9. Global Pipes
Setting up application-wide pipes:
Method 1: Using useGlobalPipes()
import { ValidationPipe } from "@nestjs/common";
async function bootstrap() { const app = await NestFactory.create(AppModule);
app.useGlobalPipes( new ValidationPipe({ whitelist: true, // Strip properties not in DTO forbidNonWhitelisted: true, // Throw error for extra properties transform: true, // Transform payloads to DTO instances disableErrorMessages: false, // Show detailed error messages transformOptions: { enableImplicitConversion: true, // Auto-convert types }, }) );
await app.listen(3000);}bootstrap();Method 2: Dependency Injection (Recommended)
import { Module } from "@nestjs/common";import { APP_PIPE } from "@nestjs/core";import { ValidationPipe } from "@nestjs/common";
@Module({ providers: [ { provide: APP_PIPE, useClass: ValidationPipe, }, ],})export class AppModule {}Multiple Global Pipes
@Module({ providers: [ { provide: APP_PIPE, useClass: ValidationPipe, }, { provide: APP_PIPE, useClass: TransformPipe, }, ],})export class AppModule {}Conditional Global Pipes
import { Provider } from "@nestjs/common";import { APP_PIPE } from "@nestjs/core";
export const conditionalPipeProvider: Provider = { provide: APP_PIPE, useFactory: () => { if (process.env.NODE_ENV === "development") { return new ValidationPipe({ disableErrorMessages: false, skipMissingProperties: false, }); } return new ValidationPipe({ disableErrorMessages: true, skipMissingProperties: true, }); },};10. Advanced Pipe Techniques
Async Pipes
Pipes can be asynchronous for database lookups or external API calls:
@Injectable()export class AsyncValidationPipe implements PipeTransform { constructor(private userService: UserService) {}
async transform(value: any, metadata: ArgumentMetadata) { // Async validation logic const exists = await this.userService.emailExists(value.email); if (exists) { throw new ConflictException("Email already exists"); } return value; }}Conditional Validation
@Injectable()export class ConditionalValidationPipe implements PipeTransform { transform(value: any, metadata: ArgumentMetadata) { const { type, data } = metadata;
// Only validate body parameters if (type === "body") { return this.validateBody(value); }
// Only validate specific parameter names if (data === "email") { return this.validateEmail(value); }
return value; }
private validateBody(value: any) { // Body validation logic return value; }
private validateEmail(value: string) { const emailRegex = /^[^\s@]+@[^\s@]+\.[^\s@]+$/; if (!emailRegex.test(value)) { throw new BadRequestException("Invalid email format"); } return value; }}Metadata-aware Pipes
@Injectable()export class MetadataAwarePipe implements PipeTransform { transform(value: any, metadata: ArgumentMetadata) { console.log("Metadata:", metadata); /* { type: 'body' | 'query' | 'param' | 'custom', metatype: [Function: CreateCatDto], data: undefined } */
if (metadata.metatype === CreateCatDto) { // Specific validation for CreateCatDto return this.validateCreateCatDto(value); }
return value; }
private validateCreateCatDto(value: any) { // Custom validation logic for CreateCatDto return value; }}Pipe Chaining
@Get(':id')async findOne( @Param('id', ParseIntPipe, PositiveNumberPipe, ExistsValidationPipe) id: number) { return this.catsService.findOne(id);}
// Execution order: ParseIntPipe -> PositiveNumberPipe -> ExistsValidationPipe11. Best Practices
1. Use Built-in Pipes When Possible
// Preferred: Use built-in ParseIntPipe@Get(':id')async findOne(@Param('id', ParseIntPipe) id: number) { return this.catsService.findOne(id);}
// Avoid: Custom implementation when built-in exists@Get(':id')async findOne(@Param('id', CustomParseIntPipe) id: number) { return this.catsService.findOne(id);}2. Prefer Class-based Registration
// Preferred: Class-based registration@UsePipes(ValidationPipe)
// Avoid: Instance-based registration (unless configuration needed)@UsePipes(new ValidationPipe())3. Global vs Scoped Pipes
// Global pipes for common validationapp.useGlobalPipes(new ValidationPipe());
// Scoped pipes for specific validation@Post()@UsePipes(new SpecificValidationPipe())async create(@Body() data: CreateDto) { }4. Error Handling Best Practices
@Injectable()export class ValidationPipe implements PipeTransform { transform(value: any, metadata: ArgumentMetadata) { try { // Validation logic return this.validate(value); } catch (error) { // Provide clear, helpful error messages throw new BadRequestException({ message: "Validation failed", field: metadata.data, expectedType: metadata.type, receivedValue: value, }); } }}5. Type Safety
// Use proper TypeScript types@Injectable()export class TypedPipe implements PipeTransform<string, number> { transform(value: string, metadata: ArgumentMetadata): number { const result = parseInt(value, 10); if (isNaN(result)) { throw new BadRequestException("Expected numeric string"); } return result; }}6. Reusable Validation Logic
// Create reusable validation functionsexport class ValidationUtils { static validateEmail(email: string): boolean { const emailRegex = /^[^\s@]+@[^\s@]+\.[^\s@]+$/; return emailRegex.test(email); }
static validatePhoneNumber(phone: string): boolean { const phoneRegex = /^\+?[\d\s-()]+$/; return phoneRegex.test(phone); }}
@Injectable()export class ContactValidationPipe implements PipeTransform { transform(value: any, metadata: ArgumentMetadata) { if (value.email && !ValidationUtils.validateEmail(value.email)) { throw new BadRequestException("Invalid email format"); }
if (value.phone && !ValidationUtils.validatePhoneNumber(value.phone)) { throw new BadRequestException("Invalid phone number format"); }
return value; }}12. Real-world Examples
Example 1: E-commerce Product Validation
import { IsString, IsNumber, IsOptional, Min, Max, IsArray, ValidateNested, Type,} from "class-validator";
export class ProductImageDto { @IsString() url: string;
@IsString() altText: string;}
export class CreateProductDto { @IsString() @Length(1, 100) name: string;
@IsString() @Length(10, 1000) description: string;
@IsNumber({ maxDecimalPlaces: 2 }) @Min(0.01) @Max(999999.99) price: number;
@IsNumber() @Min(0) stock: number;
@IsArray() @ValidateNested({ each: true }) @Type(() => ProductImageDto) images: ProductImageDto[];
@IsArray() @IsString({ each: true }) @IsOptional() tags?: string[];}
// Custom pipes for product validation@Injectable()export class ProductSkuGeneratorPipe implements PipeTransform { transform(value: CreateProductDto, metadata: ArgumentMetadata) { // Generate SKU based on product name const sku = value.name .toLowerCase() .replace(/[^a-z0-9]/g, "-") .replace(/-+/g, "-") .replace(/^-|-$/g, "");
return { ...value, sku: `${sku}-${Date.now()}`, }; }}
@Injectable()export class PriceValidationPipe implements PipeTransform { async transform(value: CreateProductDto, metadata: ArgumentMetadata) { // Check if price is competitive const category = await this.categoryService.findByName(value.category); const avgPrice = await this.productService.getAveragePrice(category.id);
if (value.price > avgPrice * 2) { throw new BadRequestException( `Price ${value.price} is significantly higher than category average ${avgPrice}` ); }
return value; }}
// Usage in controller@Controller("products")export class ProductsController { @Post() @UsePipes(ValidationPipe, ProductSkuGeneratorPipe, PriceValidationPipe) async create(@Body() createProductDto: CreateProductDto) { return this.productService.create(createProductDto); }}Example 2: File Upload Validation Pipeline
@Injectable()export class FileTypeValidationPipe implements PipeTransform { private readonly allowedMimeTypes = [ 'image/jpeg', 'image/png', 'image/gif', 'application/pdf', ];
transform(value: Express.Multer.File, metadata: ArgumentMetadata) { if (!this.allowedMimeTypes.includes(value.mimetype)) { throw new BadRequestException( `File type ${value.mimetype} not allowed. Allowed types: ${this.allowedMimeTypes.join(', ')}` ); } return value; }}
@Injectable()export class FileSizeValidationPipe implements PipeTransform { constructor(private readonly maxSizeInMB: number) {}
transform(value: Express.Multer.File, metadata: ArgumentMetadata) { const maxSizeInBytes = this.maxSizeInMB * 1024 * 1024;
if (value.size > maxSizeInBytes) { throw new BadRequestException( `File size ${(value.size / 1024 / 1024).toFixed(2)}MB exceeds limit of ${this.maxSizeInMB}MB` ); } return value; }}
@Injectable()export class ImageDimensionValidationPipe implements PipeTransform { async transform(value: Express.Multer.File, metadata: ArgumentMetadata) { if (!value.mimetype.startsWith('image/')) { return value; // Skip non-images }
const dimensions = await this.getImageDimensions(value.buffer);
if (dimensions.width > 4000 || dimensions.height > 4000) { throw new BadRequestException( `Image dimensions ${dimensions.width}x${dimensions.height} exceed maximum of 4000x4000` ); }
if (dimensions.width < 100 || dimensions.height < 100) { throw new BadRequestException( `Image dimensions ${dimensions.width}x${dimensions.height} below minimum of 100x100` ); }
return { ...value, metadata: { width: dimensions.width, height: dimensions.height, }, }; }
private async getImageDimensions(buffer: Buffer): Promise<{ width: number; height: number }> { // Implementation to get image dimensions // Could use sharp, jimp, or similar library return { width: 1920, height: 1080 }; // Placeholder }}
// Usage@Post('upload')@UseInterceptors(FileInterceptor('file'))async uploadFile( @UploadedFile( FileTypeValidationPipe, new FileSizeValidationPipe(10), // 10MB limit ImageDimensionValidationPipe ) file: Express.Multer.File & { metadata?: any }) { return this.fileService.save(file);}Example 3: API Pagination and Filtering
export class PaginationDto { @IsOptional() @Type(() => Number) @IsInt() @Min(1) page?: number = 1;
@IsOptional() @Type(() => Number) @IsInt() @Min(1) @Max(100) limit?: number = 10;
@IsOptional() @IsString() search?: string;
@IsOptional() @IsString() sortBy?: string;
@IsOptional() @IsEnum(['ASC', 'DESC']) sortOrder?: 'ASC' | 'DESC' = 'ASC';}
@Injectable()export class PaginationValidationPipe implements PipeTransform { transform(value: PaginationDto, metadata: ArgumentMetadata) { // Calculate offset const offset = (value.page - 1) * value.limit;
// Validate sort field if provided const allowedSortFields = ['id', 'name', 'createdAt', 'updatedAt']; if (value.sortBy && !allowedSortFields.includes(value.sortBy)) { throw new BadRequestException( `Invalid sort field. Allowed fields: ${allowedSortFields.join(', ')}` ); }
return { ...value, offset, take: value.limit, }; }}
@Injectable()export class SearchSanitizationPipe implements PipeTransform { transform(value: PaginationDto, metadata: ArgumentMetadata) { if (value.search) { // Sanitize search query value.search = value.search .trim() .replace(/[<>]/g, '') // Remove potential XSS characters .substring(0, 100); // Limit search length }
return value; }}
// Usage@Get()async findAll( @Query(ValidationPipe, PaginationValidationPipe, SearchSanitizationPipe) query: PaginationDto) { return this.catsService.findAll(query);}Testing Pipes
Unit Testing Custom Pipes
import { BadRequestException } from "@nestjs/common";import { ParseIntPipe } from "./parse-int.pipe";
describe("ParseIntPipe", () => { let pipe: ParseIntPipe;
beforeEach(() => { pipe = new ParseIntPipe(); });
it("should be defined", () => { expect(pipe).toBeDefined(); });
it("should parse valid integer string", () => { const result = pipe.transform("123", { type: "param", metatype: Number, data: "id", }); expect(result).toBe(123); });
it("should throw BadRequestException for invalid string", () => { expect(() => { pipe.transform("abc", { type: "param", metatype: Number, data: "id" }); }).toThrow(BadRequestException); });
it("should handle edge cases", () => { expect( pipe.transform("0", { type: "param", metatype: Number, data: "id" }) ).toBe(0); expect(() => { pipe.transform("", { type: "param", metatype: Number, data: "id" }); }).toThrow(BadRequestException); });});Integration Testing with Controllers
import { Test, TestingModule } from "@nestjs/testing";import { BadRequestException } from "@nestjs/common";import { CatsController } from "./cats.controller";import { CatsService } from "./cats.service";import { ValidationPipe } from "./pipes/validation.pipe";
describe("CatsController", () => { let controller: CatsController; let service: CatsService;
beforeEach(async () => { const module: TestingModule = await Test.createTestingModule({ controllers: [CatsController], providers: [ { provide: CatsService, useValue: { create: jest.fn(), findAll: jest.fn(), findOne: jest.fn(), }, }, ], }).compile();
controller = module.get<CatsController>(CatsController); service = module.get<CatsService>(CatsService); });
describe("create", () => { it("should create a cat with valid data", async () => { const createCatDto = { name: "Fluffy", age: 3, breed: "persian", };
const pipe = new ValidationPipe(); const validatedData = await pipe.transform(createCatDto, { type: "body", metatype: CreateCatDto, });
expect(validatedData).toEqual(createCatDto); });
it("should throw error with invalid data", async () => { const invalidDto = { name: "", age: -1, breed: "persian", };
const pipe = new ValidationPipe();
await expect( pipe.transform(invalidDto, { type: "body", metatype: CreateCatDto, }) ).rejects.toThrow(BadRequestException); }); });});Summary
Pipes in NestJS are essential components for data transformation and validation:
- Built-in pipes handle common transformation and validation scenarios
- Custom pipes implement specific business logic and validation rules
- Multiple scopes (parameter, method, controller, global) provide flexibility
- Schema validation with Zod, Joi, or class-validator offers robust validation
- Async pipes enable database lookups and external API validation
- Proper error handling provides clear feedback to API consumers
Remember to:
- Use built-in pipes when possible for common scenarios
- Implement custom pipes for specific business logic
- Prefer class-based registration for dependency injection
- Provide clear, helpful error messages
- Test pipes thoroughly in isolation and integration
- Consider performance implications for global pipes
- Use TypeScript types for better type safety
Pipes are crucial for building robust, secure NestJS applications that properly validate and transform incoming data before it reaches your business logic.
Key Takeaways
- Transformation: Convert input data to desired formats (string to number, ID to entity)
- Validation: Ensure data meets business rules and constraints
- Built-in Pipes: Use ParseIntPipe, ValidationPipe, ParseUUIDPipe, etc. for common cases
- Custom Pipes: Implement PipeTransform interface for specific logic
- Global Registration: Use APP_PIPE token for dependency injection
- Schema Validation: Leverage Zod, Joi, or class-validator for comprehensive validation
- Error Handling: Pipes throw exceptions that are caught by exception filters
- Type Safety: Use proper TypeScript types for better development experience
